

|
|
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |
This line indicates that any connection received on port 110 (Post Office Protocol) from the 206.116.65 network is to be connected to 198.53.64.14. Additional options for the rule allow for the specification of a privileged port number. Few services actually require these. The final option allows for the specification of an alternate port number should the same service be running on a different port number at the remote end.
As with the other services, the host pattern that is specified with the port command allows for both the allowed and non-allowed network or host IP addresses to be specified.
The NNTP news protocol is used for reading Internet newsgroups. This protocol also performs news feeds and is often used to provide news reading services at the workstation level. The configuration of the plug-gw proxy for an Internet news feed is essentially the same as the configuration for a news reader.
In both cases, the NNTP port is defined in the etc/services file as 119. You must configure the plug-gw line as follows:
plug-gw: port 119 206.116.65.* -plug-to 198.53.64.1
This means that any connections received on port 119 from the local LAN will be directed to the same port on the system at 198.53.64.1.The two major reasons for handling NNTP with plug-gw are to allow NNTP client access through the firewall, and to allow for a news feed.
For the firewall to accept news connections, inetd must be configured to start the plug-gw application whenever a connection request is made for the NNTP port. This is done by adding the following line to the /etc/inetd.conf file and restarting inetd:
nntp stream tcp nowait root /usr/local/etc/plug-gw plug-gw 119
If you configure plug-gw but forget this step, the TIS firewall Toolkit will seem not to operate—no log messages will print to the files or to the console.
To configure an NNTP client, such as WinVN for the PC-based architecture, you must set up WinVN so that it knows where to connect. Normally, this would be the actual NNTP server that you want to access, but in this case, it is the name or IP address of the firewall. On the firewall, the appropriate line in the netperm-table file must be included to specify where the NNTP client requests are to go. If several NNTP servers are available for reading news, you may want to separate them onto different network ports on the firewall, so that traffic can be sent to the different sites. Consider this sample part of the netperm-table file:
plug-gw: port 2119 206.116.65.* -plug-to 198.53.64.1 -port 119 plug-gw: port 2120 206.116.65.* -plug-to 198.53.64.5 -port 119
In this scenario, when users want to read news from the 198.53.64.5 server, they must connect to the firewall on port 2120. Figure 6.3 illustrates the configuration of the WinVN client for access to news through the firewall.
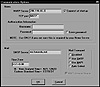
Figure 6.3 Configuring WinVN to use the NNTP proxy.
Regardless of the news reader client software that you use, it needs to be configured to use the firewall as the connection point or news host.
What if different news servers are available that your hosts are permitted to connect to? How does the system administrator configure multiple hosts at the same TCP/IP service port? The answer is to specify a different port on the firewall, and let plug-gw redirect to the correct port on the remote system. This is done by using a rule in the netperm-table file:
plug-gw: port 2120 206.116.65.* -plug-to 198.53.64.5 -port 119
According to this command, if a connection on port 2120 is requested, redirect that request on port 119 or the host at 198.53.64.5. This is only part of the solution. The /etc/services file should also be edited to add a news NNTP service entry to show the new service port for this connection. For example, the following line specifies that the service nntp-a is on port 2120:
nntp-a 2120/tcp readnews untp # USENET News Transfer Protocol
The next step is to tell inetd that connections on this port are to be sent to the plug-gw application. This is done by adding the following line to the /etc/inetd.conf file and restarting inetd.
nntp-a stream tcp nowait root /usr/local/etc/plug-gw plug-gw 2120
When the user wants to use this alternate server, he or she must reconfigure the news client software, as shown in figure 6.4, to point to the new services port.
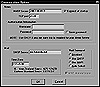
Figure 6.4 Configuring WinVN and NNTP.
Although you can set up your firewall so that NNTP clients can read news, this is generally not a popular setup. A much more realistic configuration would be for the clients to interact with a local news server. This configuration requires the firewall to allow for a news feed to be passed through to the internal news server.
To do this, the external news server and the internal news client must be set up so that they pass their information through the firewall. The trick is understanding what configuration information must be placed in the news server configuration files on both ends. For the purpose of this discussion, assume that the news server software in use is INN 1.4. The file hosts.nntp provides information regarding what hosts are permitted to connect to the INN NNTP server. Consider the news server and firewall configuration shown in figure 6.5.
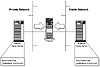
Figure 6.5 News client and server.
Normally, the hosts.nntp file on each news server contains the name or IP address of the other news server that is allowed to connect to it. In this case, the name of the machine that goes in both hosts.nntp files is in fact the name or IP address of the firewall. This is because the firewall actually establishes a connection from one network to the other, and from one server to the other using the correct service port. With the hosts.nntp file correctly configured, there will be no problems passing news through the firewall.
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |