Securing-Optimizing-RH-Linux-1_2_19
Comments and suggestions concerning this book should be mailed to gmourani@videotron.ca
© Copyright 1999-2000 Gerhard Mourani and Open Network Architecture ®
19
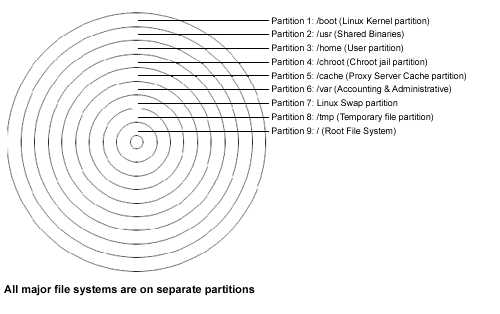
a separate partition for each major file system. This enhances security and prevents accidental
denial of service or exploit of SUID programs.
Creating multiple partition offer you the following advantages:
·
Protection against denial of service attack.
·
Protection against SUID programs.
·
Faster booting.
·
Easy backup and upgrade management.
·
Ability for better control of mounted file system.
·
Limit each file system’s ability to grow.
Warning: If previous file system or operating system exist on the hard drive and computer where
you want to install your Linux system, we highly recommend, that you make a backup of your
current system before proceeding with the disk partitioning.
Step 1
For performance, stability and security reasons you must create something like the following
partitions listed bellow on your computer. We suppose for this partition configuration the fact that
you have a SCSI hard drive of 3.2 G. Of course you will need to adjust partition sizes according to
your own needs and disk size.
Partitions that must be created on your system:
/boot
5MB
Kernel images are kept here.
/usr
1000MB
Must be large, since all linux binaries programs are installed there.
/home
500MB
Proportional to the number of users you are intended to host. (e.i. 10MB per
users * by the number of users 50 = 500MB).
/chroot
400MB
If you want to install programs in chroot jail environement. (e.i. DNS).
/cache
400MB
This is the cache partition of a proxy server. (e.i. Squid).
/var
200MB
Contains files that change when the system run normally. (e.i. log files).
<Swap>
150MB
Our swap partition. The virtual memory.
/tmp
100MB
Our temporary files partition.
/
315MB
Our root partition.