
nt-part2_44

 Analysis of the Security of Windows NT
1 March 1999
44
The auditing is based on audit records constructed on request from the responsible sub-
system or server by SRM (in some cases by LSA). Requests from the executive is
always carried out while servers need the Audit privilege for SRM to honour there
request. The request must be sent for each occurrence of an event. The audit record is
then sent to the LSA, which in turn sends it to the Event Logger after it expanded some
fields and compressed others. The final writing to disk is made by the Event Logger.
The audit record contains the following header information [43]:
• Time event was generated
• SID associated with the process causing event to be generated. If impersonating this
is the impersonating SID (both primary and impersonation SID are stored in the
body)
• Name of component or module that submitted the event
• Event ID
• Event type: error, warning, success, information, success audit, failure audit
• Event Category
• Computer
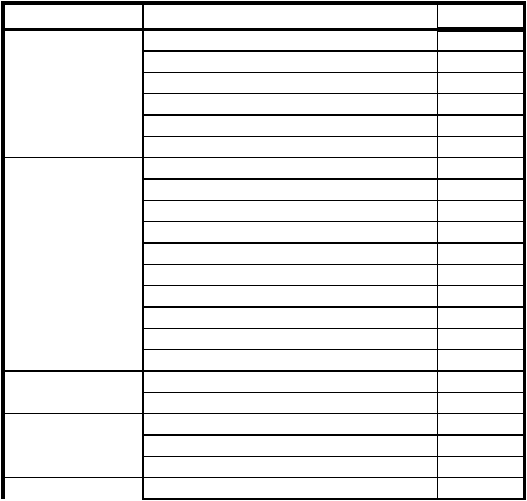
TABLE 4. Audit event types
Category
Event Type
Constructor
System
System Restart
SRM
System Shutdown
SRM
Authentication Package Loaded
LSA
Registered Logon Process
LSA
AuditLog Cleared
SRM
#Audits Discarded (due to full internal queues)
SRM
Logon/Logoff
Logon Successful
LSA
Unknown User or Password
LSA
Time Restricted Logon Failure
LSA
Account Disabled
LSA
Account Expired
LSA
Invalid Workstation
LSA
LogonType Restricted
LSA
Password Expired
LSA
Failed Logon
LSA
Logoff
LSA
Object Access
Open Object
SRM
Close Handle
SRM
Privilege Use
Assign Special Privileges
SRM
Privileged Service
SRM
Privileged Object Access
SRM
Detailed Tracking
Process Created
SRM
Analysis of the Security of Windows NT
1 March 1999
44
The auditing is based on audit records constructed on request from the responsible sub-
system or server by SRM (in some cases by LSA). Requests from the executive is
always carried out while servers need the Audit privilege for SRM to honour there
request. The request must be sent for each occurrence of an event. The audit record is
then sent to the LSA, which in turn sends it to the Event Logger after it expanded some
fields and compressed others. The final writing to disk is made by the Event Logger.
The audit record contains the following header information [43]:
• Time event was generated
• SID associated with the process causing event to be generated. If impersonating this
is the impersonating SID (both primary and impersonation SID are stored in the
body)
• Name of component or module that submitted the event
• Event ID
• Event type: error, warning, success, information, success audit, failure audit
• Event Category
• Computer
TABLE 4. Audit event types
Category
Event Type
Constructor
System
System Restart
SRM
System Shutdown
SRM
Authentication Package Loaded
LSA
Registered Logon Process
LSA
AuditLog Cleared
SRM
#Audits Discarded (due to full internal queues)
SRM
Logon/Logoff
Logon Successful
LSA
Unknown User or Password
LSA
Time Restricted Logon Failure
LSA
Account Disabled
LSA
Account Expired
LSA
Invalid Workstation
LSA
LogonType Restricted
LSA
Password Expired
LSA
Failed Logon
LSA
Logoff
LSA
Object Access
Open Object
SRM
Close Handle
SRM
Privilege Use
Assign Special Privileges
SRM
Privileged Service
SRM
Privileged Object Access
SRM
Detailed Tracking
Process Created
SRM


