

|
|
Initiation responsibility: Head of IT Section, IT Security Management
Implementation responsibility: Administrators
Users can connect to local Windows NT systems from remote IT systems via RAS (Remote Access Service). For this, the RAS-client must be installed on the remote IT system and the RAS-server on the local IT system which accepts the remote connection. Using RAS, these users can work as if they were directly connected to the network. The remote clients use standard programmes to access resources. With the help of the File-Manager or Explorer, network drives and printers are, for example, connected. These connections are permanent, i.e. users do not have to recreate connections to network resources during one session. As clients, the systems Windows NT, Windows 95, WfW, MS-DOS and OS/2 are supported.
The user creates the connection to the RAS-server with a local modem, X.25 or ISDN-card. The RAS-server, which is run on the Windows NT server, authenticates and serves the user until either he or the administrator terminates the session. The RAS connection provides all the services (file and printer sharing, database access and notifications) that are normally available to a user connected via a LAN.
Access to the RAS is provided for the whole pool of Windows NT user accounts. With the User-Manager, permission to dial in to the local network can be provided to single users, user groups or all users. Furthermore, RAS administration offers an option which allows access either to all resources which the RAS host can access within the network, or only to the resources available on the local computer. The users then use their domain log-on to create a connection via RAS. Once the user's access permission has been checked by the RAS, he can use the local resources or, if he has been granted the appropriate permission, the resources in the whole domain as well as in trusted domains.
Via the Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) the Remote Access Server provides the securest form of encrypted access permission which is supported by the server as well as the client. CHAP allows the RAS server to systematically make a selection from the securest encryption mechanism to the most insecure procedure of plain-text transmission and it protects transmitted passwords in the process.
CHAP allows the employment of diverse encryption algorithms. RAS in particular uses the cryptographic algorithm MD5. RAS refers to DES encryption for authentication if the client and the server work with RAS. For data communication, Windows NT, Windows for Workgroups and Windows 95 select among themselves the DES encrypted confirmation of authenticity. When connecting to external RAS servers or client software, a confirmation of authenticity is possible with SPAP or unencrypted text, if the external product does not support an encrypted confirmation of authenticity.
MD5, an encryption scheme installed by diverse PPP implementations for encrypted confirmations of authenticity, can be selected from the Microsoft RAS-Client if a connection to other RAS servers exists.
PAP works with simple, unencrypted passwords, thereby offering little in the way of responsible protocol for confirmations of authenticity. This protocol will normally only be selected if the external workstation and the server cannot agree on a form of encryption that offers more security.
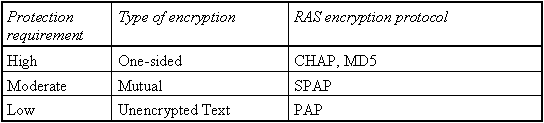
Depending upon which level of protection is required, the RAS encryption protocol should be selected according to the following table, so that at least the relevant protocol given below is deployed. This can mean that, if the security demands are high, the use of clients not supporting the required protocol must be ruled out.
Data encryption protects data and ensures a secure dial-up connection. The RAS administrator can set up the RAS server in such a way that the transmission of data always takes place in encrypted form. Users connected to this server automatically encrypt all data sent.
Note: This option requires that all connected clients know how to encrypt data. In this case as, for example, in a homogeneous Windows NT network, this option must in any case be activated.
The start options for RAS are set under the control panel option " Services ", and the configuration takes place via the control panel option " Network ", where the choice of authentication procedure also takes place. By choosing the option " Only Microsoft-encrypted confirmation of authenticity ", the choice of CHAP can be forced by MD5; the encryption for data can additionally be activated. Under the german version of Windows NT transmitted data is then not encrypted with DES but with RC4.
RAS supports the security-hosts of other manufacturers, whereby the security-host switches between the remote user and the RAS server. A security host is an additional computer in the network, which offers security services such as support for chip cards. A security host of this type generally offers an extra security level by demanding an identity card for confirmation of authenticity, or by supporting similarly strong authentication procedures, before allowing access to the RAS Server.
Access supervision via call-back is an additional safeguard offered by RAS. With this function the system administrator can demand that a certain remote user dials from a previously determined place (e.g. private telephone line) or that this user can be dialled from anywhere. With access supervision via call-back, the user initialises a call and makes a connection with the RAS server. The RAS server then hangs up and momentarily calls the previously-given call-back number. When using an analogue telephone network call-back modems must be installed, where during transmission via ISDN or X.25 (e.g. Datex-P), the features of these networks can be used. However, it must be borne in mind that the security of the partner identification is no longer ensured when changing the X.25 carrier, i.e. with data transmission crossing country borders.
Under RAS the system administrator controls remote access to the network. Further to the service programmes that are delivered with the Windows NT server package, the service programme RAS-Administration offers the administrator the possibility to remove or provide access permissions for single users and/or groups. This means that access to the network must be explicitly provided for every user accessing the network via RAS, although RAS is running on a Windows NT server computer. This process ensures not only that remote access must be explicitly permitted, but also allows call-back restrictions to be defined.
RAS offers an additional security level. RAS-Administration offers an option which allows access to all resources that the RAS host detects, or to the available resources on the local computer. The administrator can thus control which data is available to a remote user. If possible, permission for access to further computers in the network should either be provided restrictively or not at all, in order to limit possible damage when security barriers have been broken.
Note: If RAS is used in a domain, changes to RAS permission will not immediately take effect on all servers. It can take up to 15 minutes for a change to be replicated on all servers in the domain. If required, the domains can be explicitly synchronised anew, to ensure that a user whose permissions have been removed, no longer has access to the network until the change has been replicated.
Additional controls:
| © Copyright
by Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik |
July 1999 |