

|
|
Initiation responsibility: Head of IT Section, IT Security Management
Implementation responsibility: Administrators
The regulations laid down for the logging of events relevant to security can be implemented using the " Policy " option of User Manager. In general, suitable regulations for average protection requirements correspond to those in the following diagram:
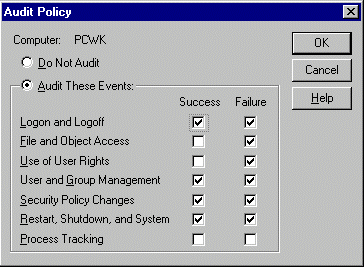
In addition, if data with higher protection requirements is stored and/or processed on a computer, then successful and rejected file and object accesses should still be recorded. This recording should be limited to files containing information which is particularly worth protecting, together with the programs required for processing these files, so that the log file does not become so extensive that it can no longer be evaluated at acceptable expense.
Where higher security requirements exist, accesses and access attempts to the registry, at least for the keys HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE and HKEY_USERS, should also be recorded. In the process it is advisable to record all rejected attempts and, among the successful ones, at least the following ones which can lead to changes in the registry:
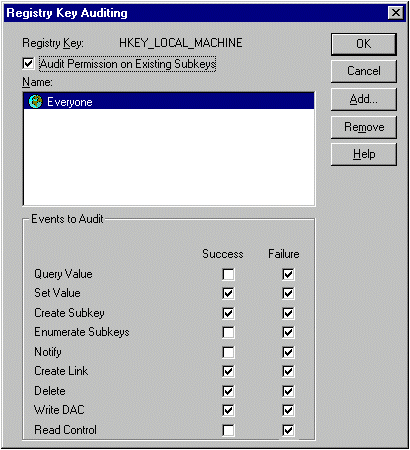
It should be noted that accesses to the registry are only recorded if the auditing of file and object accesses is activated in the General Audit Policy.
When access to the registry is monitored, a large amount of auditing data is generated which must also be evaluated. Furthermore, recording these events usually has a negative effect on the system performance. In some cases, taking the security requirements into account, the following alternative procedure is recommended. Rejected attempts to access the keys HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE and HKEY_USERS, are recorded as described above. Successful accesses to these keys are not recorded. Rather, a suitable integrity protection program is used. In this way, changes to these keys are easily recognised. However, the disadvantage of this method is that the program does not recognise who has made the changes.
By stipulating appropriate specifications with the utility Event display,the log file should be created to be so large that all entries occurring within a specified period (for example, in one week) can be stored reliably. When doing this, provision should be made for a security margin, so that in general a maximum of around 30% of the log file is filled. After the specified period has elapsed, each log file should be analysed, filed and then cleared to create space for new entries.
In order to avoid system failures as a result of fully writing the log file, under normal circumstances one of the options " Overwrite events as needed " or " Overwrite events older than x days " should be chosen, choosing for x the length of the specified filing cycle, e.g. 30 days:
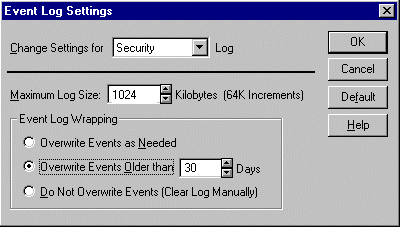
For systems where enhanced security requirements exist, the option " Do not overwrite events (clear log manually) " should instead be chosen. However, when the log overflows this leads to a system standstill and then causes corresponding expense.
The logs are evaluated using the management program Event display, which enables the specific evaluation of procedures critical to security to take place through the selection of suitable filter rules:
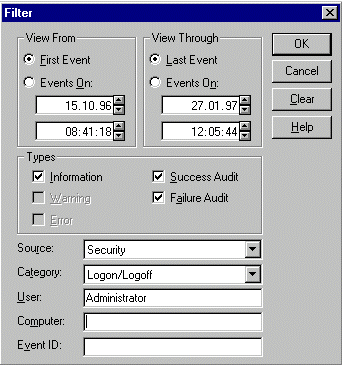
Evaluation of the security log should follow a suitable, generally binding checklist (see S 2.64 Checking of log files and S 2.92 Performing security checks in the Windows NT client-server network).
Additional controls:
| © Copyright
by Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik |
July 1999 |