

|
|
Initiation responsibility: Head of IT Section, IT Security Management
Implementation responsibility: Administrators; persons responsible for substantive tasks
Such access permissions determine which person will, on the basis of his/her function, be authorised to use applications or data. The access permissions (e.g. read, write, execute) to IT applications, parts of applications, or data, depend on the function fulfilled by the given person, e.g. application supervisor, scheduler, system program, application developer, system administrator, auditor, data acquisition operator, desk officer. In any case, only so many access permissions as are required for task performance (need-to-know principle) should be granted. Enforcement of access rights must be through the administration of rights of the IT system.
A variety of IT systems allow various privileges to be defined as group privileges or as profiles (e.g. data acquisition operators). This definition corresponds to the technical implementation of privileges allocated to a function. It is beneficial for the administration of the privileges of an IT system to compile such groups or profiles, thus considerably simplifying the allocation and updating of privileges.
The person responsible in each given case must arrange for, and document, the assignment of, and changes in, access privileges. Such documentation must show:
Additional controls:
The approach to the separation of functions and granting of privileges is illustrated in the following example.
The IT application considered here is a system for travel expenses accounting. The relevant rooms are shown in the graph below. The IT system consists of a LAN to which, in addition to the operator's console, three PCs are connected as workstations.
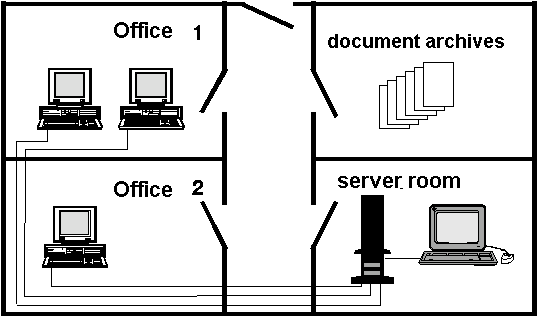
Step 1: Division of responsibilities and separation of functions
The following functions are required for the travel expenses accounting system considered here:
The following functions are not compatible with each other on account of inherent necessities:
These functions are performed by the following persons:
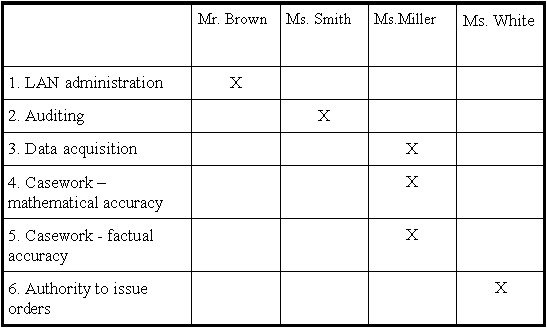
Step 2: Granting of room access permissions
The protection requirement of the various rooms is described below and the granting of room access permissions documented in the table:
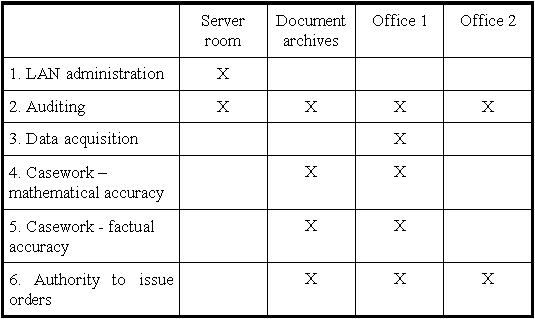
Step 3: Granting of (system/network) access privileges
According to functions, the following access privileges are assigned:
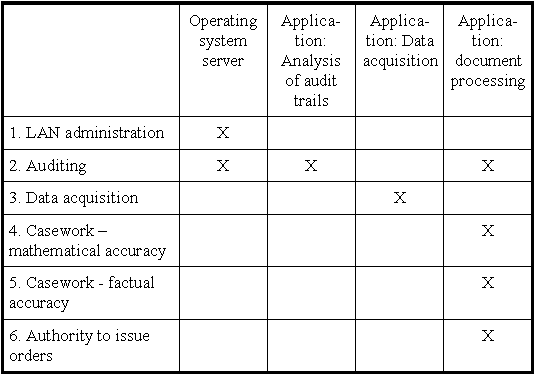
Step 4: Granting of (application/data) access permissions
In the following, the (application/data) access privileges required for the execution of a function are set out. Legend:
E = right to Execute an application/software
R = right to Read data
W = right to Write data, i.e. generate data
M = right to Modify data
D = right to Delete data
S = Right to Sign orders to pay
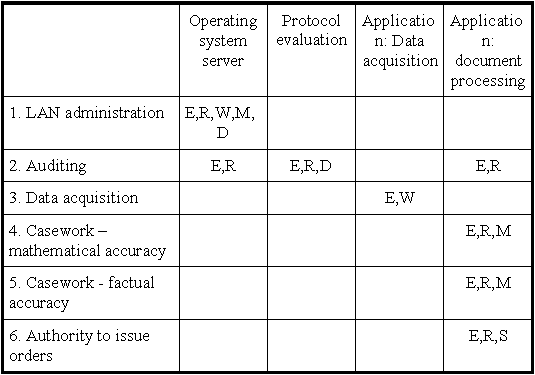
Documentation of this kind facilitates the assignment of privileges. Assuming job changing by Ms. Smith, the vacancy thus having to be filled, the above tables can be used to determine which of Ms. Smith's former privileges must be revoked and assigned to the new staff member. If the latter, qua substitute, additionally is to perform the function "casework, including authority to issue orders", the required assignment of privileges elucidates the conflict arising from the fact that the new staff member, when acting as a substitute, can carry out unnoticed manipulations.
| © Copyright
by Bundesamt für Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik |
July 1999 |